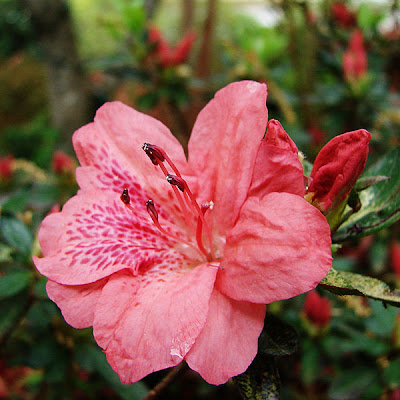
Rubus Berry Plants
Fruit
Rubus Berry Plants
Fruit
In broad terms, a Fruit is a structure of a Plants that contains its seeds.
The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain Plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state, such as apples, oranges, grapes, strawberries, juniper berries and bananas. seed-associated structures that do not fit these informal criteria are usually called by other names, such as vegetables, pods, nut, ears and cones.
In biology (botany), a "fruit" is a part of a Flowering plant that derives from specific tissues of the flower, mainly one or more ovaries. Taken strictly, this definition excludes many structures that are "fruits" in the common sense of the term, such as those produced by non-Flowering plants (like juniper berries, which are the seed-containing female cones of conifers), and fleshy fruit-like growths that develop from other plant tissues close to the fruit (accessory fruit, or more rarely false fruit or pseudocarp), such as cashew fruits. Often the botanical fruit is only part of the common fruit, or is merely adjacent to it. On the other hand, the botanical sense includes many structures that are not commonly called "fruits", such as bean pods, corn kernels, wheat grains, tomatoes, and many more. However, there are several variants of the biological definition of fruit that emphasize different aspects of the enormous variety that is found among plant fruits.
fruits (in either sense of the word) are the means by which many plants disseminate seeds. Most edible fruits, in particular, were evolved by plants in order to exploit animals as a means for seed dispersal, and many animals (including humans to some extent) have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. fruits account for a substantial fraction of world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings.
Fungus also have fruit. When a Fungus begins to produce spores, the section of the fungus producing the spores is called the fruiting body of the fungus.
Simple fruit
Simple fruits can be either dry or fleshy, and result from the ripening of a simple or compound ovary in a flower with only one pistil. Dry fruits may be either dehiscent (opening to discharge seeds), or indehiscent (not opening to discharge seeds). Types of dry, simple fruits, with examples of each, are:
* achene - Most commonly seen in aggregate fruits (e.g. strawberry)
* capsule – (Brazil nut)
* caryopsis – (wheat)
* Cypsela - An achene-like fruit derived from the individual florets in a capitulum (e.g. dandelion).
* fibrous drupe – (coconut, walnut)
* follicle – is formed from a single carpel, and opens by one suture (e.g. milkweed). More commonly seen in aggregate fruits (e.g. magnolia)
* legume – (pea, bean, peanut)
* loment - a type of indehiscent legume
* nut – (hazelnut, beech, oak acorn)
* samara – (elm, ash, maple key)
* schizocarp – (carrot seed)
* silique – (radish seed)
* silicle – (shepherd's purse)
* utricle – (beet)
fruits in which part or all of the pericarp (fruit wall) is fleshy at maturity are simple fleshy fruits. Types of fleshy, simple fruits (with examples) are:
* berry – (redcurrant, gooseberry, tomato, cranberry)
* stone fruit or drupe (plum, cherry, peach, apricot, olive)
An aggregate fruit, or etaerio, develops from a single flower with numerous simple pistils.
* Magnolia and Peony, collection of follicles developing from one flower.
* Sweet gum, collection of capsules.
* Sycamore, collection of achenes.
* Teasel, collection of cypsellas
* Tuliptree, collection of samaras.
The pome fruits of the Family Rosaceae, (including apples, pears, rosehips, and saskatoon berry) are a syncarpous fleshy fruit, a simple fruit, developing from a half-inferior ovary.
Schizocarp fruits form from a syncarpous ovary and do not really dehisce, but split into segments with one or more seeds; they include a number of different forms from a wide range of families. Carrot seed is an example.
The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain Plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state, such as apples, oranges, grapes, strawberries, juniper berries and bananas. seed-associated structures that do not fit these informal criteria are usually called by other names, such as vegetables, pods, nut, ears and cones.
In biology (botany), a "fruit" is a part of a Flowering plant that derives from specific tissues of the flower, mainly one or more ovaries. Taken strictly, this definition excludes many structures that are "fruits" in the common sense of the term, such as those produced by non-Flowering plants (like juniper berries, which are the seed-containing female cones of conifers), and fleshy fruit-like growths that develop from other plant tissues close to the fruit (accessory fruit, or more rarely false fruit or pseudocarp), such as cashew fruits. Often the botanical fruit is only part of the common fruit, or is merely adjacent to it. On the other hand, the botanical sense includes many structures that are not commonly called "fruits", such as bean pods, corn kernels, wheat grains, tomatoes, and many more. However, there are several variants of the biological definition of fruit that emphasize different aspects of the enormous variety that is found among plant fruits.
fruits (in either sense of the word) are the means by which many plants disseminate seeds. Most edible fruits, in particular, were evolved by plants in order to exploit animals as a means for seed dispersal, and many animals (including humans to some extent) have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. fruits account for a substantial fraction of world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings.
Fungus also have fruit. When a Fungus begins to produce spores, the section of the fungus producing the spores is called the fruiting body of the fungus.
Simple fruit
Simple fruits can be either dry or fleshy, and result from the ripening of a simple or compound ovary in a flower with only one pistil. Dry fruits may be either dehiscent (opening to discharge seeds), or indehiscent (not opening to discharge seeds). Types of dry, simple fruits, with examples of each, are:
* achene - Most commonly seen in aggregate fruits (e.g. strawberry)
* capsule – (Brazil nut)
* caryopsis – (wheat)
* Cypsela - An achene-like fruit derived from the individual florets in a capitulum (e.g. dandelion).
* fibrous drupe – (coconut, walnut)
* follicle – is formed from a single carpel, and opens by one suture (e.g. milkweed). More commonly seen in aggregate fruits (e.g. magnolia)
* legume – (pea, bean, peanut)
* loment - a type of indehiscent legume
* nut – (hazelnut, beech, oak acorn)
* samara – (elm, ash, maple key)
* schizocarp – (carrot seed)
* silique – (radish seed)
* silicle – (shepherd's purse)
* utricle – (beet)
fruits in which part or all of the pericarp (fruit wall) is fleshy at maturity are simple fleshy fruits. Types of fleshy, simple fruits (with examples) are:
* berry – (redcurrant, gooseberry, tomato, cranberry)
* stone fruit or drupe (plum, cherry, peach, apricot, olive)
An aggregate fruit, or etaerio, develops from a single flower with numerous simple pistils.
* Magnolia and Peony, collection of follicles developing from one flower.
* Sweet gum, collection of capsules.
* Sycamore, collection of achenes.
* Teasel, collection of cypsellas
* Tuliptree, collection of samaras.
The pome fruits of the Family Rosaceae, (including apples, pears, rosehips, and saskatoon berry) are a syncarpous fleshy fruit, a simple fruit, developing from a half-inferior ovary.
Schizocarp fruits form from a syncarpous ovary and do not really dehisce, but split into segments with one or more seeds; they include a number of different forms from a wide range of families. Carrot seed is an example.
Related : Fruit From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, Rubus Berry Plants















 9:26 AM
9:26 AM
 Goohara
Goohara