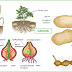
Rubus Berry Plants
Sexual Reproduction
Rubus Berry Plants
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction is characterized by processes that pass a combination of genetic material to offspring, resulting in increased genetic diversity. The two main processes are: meiosis, involving the halving of the number of chromosomes; and fertilization, involving the fusion of two gametes and the restoration of the original number of chromosomes. During meiosis, the chromosomes of each pair usually cross over to achieve homologous recombination.
The evolution of Sexual Reproduction is a major puzzle. The first fossilized evidence of sexually reproducing Organisms is from eukaryotes of the Stenian period, about 1 to 1.2 billion years ago. Sexual Reproduction is the primary method of reproduction for the vast majority of macroscopic organisms, including almost all animals and Plants. Bacterial conjugation, the transfer of DNA between two bacteria, is often mistakenly confused with Sexual Reproduction, because the mechanics are similar.
A major question is why Sexual Reproduction persists when parthenogenesis appears in some ways to be a superior form of reproduction. Contemporary evolutionary thought proposes some explanations. It may be due to selection pressure on the clade itself—the ability for a population to radiate more rapidly in response to a changing environment through sexual recombination than parthenogenesis allows. Alternatively, Sexual Reproduction may allow for the "ratcheting" of evolutionary speed as one clade competes with another for a limited resource.
The evolution of Sexual Reproduction is a major puzzle. The first fossilized evidence of sexually reproducing Organisms is from eukaryotes of the Stenian period, about 1 to 1.2 billion years ago. Sexual Reproduction is the primary method of reproduction for the vast majority of macroscopic organisms, including almost all animals and Plants. Bacterial conjugation, the transfer of DNA between two bacteria, is often mistakenly confused with Sexual Reproduction, because the mechanics are similar.
A major question is why Sexual Reproduction persists when parthenogenesis appears in some ways to be a superior form of reproduction. Contemporary evolutionary thought proposes some explanations. It may be due to selection pressure on the clade itself—the ability for a population to radiate more rapidly in response to a changing environment through sexual recombination than parthenogenesis allows. Alternatively, Sexual Reproduction may allow for the "ratcheting" of evolutionary speed as one clade competes with another for a limited resource.
Plant Reproduction
Animals typically produce male gametes called sperm, and female gametes called eggs and ova, following immediately after meiosis. With the gametes produced directly by meiosis. Plants on the other hand have mitosis occurring in spores, which are produced by meiosis. The spores germinate into the gametophyte phase. The gametophytes of different groups of Plantsvary in size; angiosperms have as few as three cells in pollen, and mosses and other so called primitive Plants may have several million cells. Plants have an alternation of generations where the sporophyte phase is succeeded by the gametophyte phase. The sporophyte phase produces spores within the sporangium by meiosis.Related : Sexual Reproduction From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, Rubus Berry Plants










 8:10 AM
8:10 AM
 Goohara
Goohara












0 ความคิดเห็น:
Post a Comment