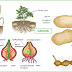
Rubus Berry Plants
Berry
Rubus Berry Plants
Berry
The botanical definition of a Berry is a fleshy Fruit produced from a single Ovary. Grapes are an example. The Berry is the most common type of fleshy fruit in which the entire Ovary wall ripens into an edible pericarp. They may have one or more carpels with a thin covering and fleshy interiors. The Seeds are usually embedded in the flesh of the Ovary. A plant that bears berries is said to be bacciferous. Many Species of Plants produce fruit that are similar to Berries but not actually Berries, and these are said to be baccate.
In everyday English, "Berry" is a term for any small edible fruit. These "Berries" are usually juicy, round or semi-oblong, brightly coloured, sweet or sour, and don't have a stone or pit, although many seeds may be present.
Many Berries, such as the Tomato, are edible, but others in the same Family, such as the fruits of the deadly nightshade (Atropa belladonna) and the fruits of the Potato (Solanum tuberosum) are poisonous to humans. Some Berries such as Capsicum have space rather than pulp around their seeds.
Examples of botanical Berries include:
* Bearberry (Arctostaphylos spp.)
* Barberry (Berberis; Berberidaceae)
* Crowberry (Empetrum spp.)
* Currant (Ribes spp.; Grossulariaceae), red, black, and white types
* Elderberry (Sambucus niger; Caprifoliaceae)
* Gooseberry (Ribes spp.; Grossulariaceae)
* Grape, Vitis vinifera
* Honeysuckle: the Berries of some Species are edible and are called honeyberries, but others are poisonous (Lonicera spp.; Caprifoliaceae)
* Lingonberry Vaccinium vitis-idaea
* Mayapple (Podophyllum spp.; Berberidaceae)
* Nannyberry or sheepberry (Viburnum spp.; Caprifoliaceae)
* Oregon-grape (Mahonia aquifolium; Berberidaceae)
* Strawberry Tree (Arbutus unedo), not to be confused with the actual strawberry (Fragaria)
* Tomato and other Species of the Family Solanaceae
* Banana
* Cranberry
* Watermelon
* Pumpkin
Berries which develop from an inferior Ovary are sometimes termed epigynous Berries or false Berries, as opposed to true Berries which develop from a superior Ovary. In so-called epigynous Berries, the Berry includes tissue derived from parts of the flower besides the Ovary. The floral tube, formed from the basal part of the sepals, petals and stamens can become fleshy at maturity and is united with the Ovary to form the fruit. Common fruits that are sometimes classified as epigynous Berries include bananas, members of the Genus Vaccinium (e.g., cranberries and blueberries), and members of the Cucurbitaceae Family (e.g., cucumbers, melons and squash).
Another specialized term is also for Cucurbitaceae fruits, which are modified to have a hard outer rind. Berries with a hard outer rind are given the special name of pepo. While pepos are most common in the Cucurbitaceae, the fruits of Passiflora and Carica are sometimes also considered pepos.
* Plum
* Peach
* Hackberry (Celtis spp.; Cannabaceae)
Other drupe-like fruits with a single seed, that lack the stony endocarp include:
* Avocado (Persea americana)
* Sea-buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides; Elaeagnaceae) A single seed inside a fleshy fruit
* Aggregate fruits, which contain seeds from different ovaries of a single flower. Examples include blackberry, Raspberry, and bayberry.
* Multiple fruits, include the fruits of multiple flowers, that are merged or packed closely together. The mulberry is a berry-like example of a multiple fruit; it develops from a cluster of tiny separate flowers that become compressed as they develop into fruit.
* Strawberry - the aggregate of seed-like Achenes is actually the "fruit", derived from an aggregate of ovaries, and the fleshy part develops from the receptacle.
* Gurbir, Duchesnea indica - structured just like a strawberry
* Sea Grape (Coccoloba uvifera; Polygonaceae) - the fruit is a dry Capsule surrounded by fleshy calyx
* Wintergreen (Gaultheria procumbens) - the fruit is a dry capsule surrounded by fleshy calyx
In everyday English, "Berry" is a term for any small edible fruit. These "Berries" are usually juicy, round or semi-oblong, brightly coloured, sweet or sour, and don't have a stone or pit, although many seeds may be present.
Many Berries, such as the Tomato, are edible, but others in the same Family, such as the fruits of the deadly nightshade (Atropa belladonna) and the fruits of the Potato (Solanum tuberosum) are poisonous to humans. Some Berries such as Capsicum have space rather than pulp around their seeds.
Botanical berries
In botanical language, a Berry is a simple fruit having seeds and pulp produced from a single Ovary; the Ovary can be inferior or superior.Examples of botanical Berries include:
* Bearberry (Arctostaphylos spp.)
* Barberry (Berberis; Berberidaceae)
* Crowberry (Empetrum spp.)
* Currant (Ribes spp.; Grossulariaceae), red, black, and white types
* Elderberry (Sambucus niger; Caprifoliaceae)
* Gooseberry (Ribes spp.; Grossulariaceae)
* Grape, Vitis vinifera
* Honeysuckle: the Berries of some Species are edible and are called honeyberries, but others are poisonous (Lonicera spp.; Caprifoliaceae)
* Lingonberry Vaccinium vitis-idaea
* Mayapple (Podophyllum spp.; Berberidaceae)
* Nannyberry or sheepberry (Viburnum spp.; Caprifoliaceae)
* Oregon-grape (Mahonia aquifolium; Berberidaceae)
* Strawberry Tree (Arbutus unedo), not to be confused with the actual strawberry (Fragaria)
* Tomato and other Species of the Family Solanaceae
* Banana
* Cranberry
* Watermelon
* Pumpkin
Modified berries
The fruit of citrus, such as the orange, kumquat and lemon, is a Berry with a thick rind and a very juicy interior that is given the special name hesperidium.Berries which develop from an inferior Ovary are sometimes termed epigynous Berries or false Berries, as opposed to true Berries which develop from a superior Ovary. In so-called epigynous Berries, the Berry includes tissue derived from parts of the flower besides the Ovary. The floral tube, formed from the basal part of the sepals, petals and stamens can become fleshy at maturity and is united with the Ovary to form the fruit. Common fruits that are sometimes classified as epigynous Berries include bananas, members of the Genus Vaccinium (e.g., cranberries and blueberries), and members of the Cucurbitaceae Family (e.g., cucumbers, melons and squash).
Another specialized term is also for Cucurbitaceae fruits, which are modified to have a hard outer rind. Berries with a hard outer rind are given the special name of pepo. While pepos are most common in the Cucurbitaceae, the fruits of Passiflora and Carica are sometimes also considered pepos.
Not a botanical berry
Many fruits commonly referred to as Berries are not actual Berries by the scientific definition, but fall into one of these categories:Drupes
Drupes are fleshy fruits produced from a (usually) single-seeded Ovary with a hard stony layer (called the endocarp) surrounding the Seed.* Plum
* Peach
* Hackberry (Celtis spp.; Cannabaceae)
Other drupe-like fruits with a single seed, that lack the stony endocarp include:
* Avocado (Persea americana)
* Sea-buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides; Elaeagnaceae) A single seed inside a fleshy fruit
Pomes
The pome Pyrinae of Family Rosaceae, such as apples and pears, have a structure (the core) that clearly separates the seeds from the Ovary tissue. However, some of the smaller pomes are sometimes referred to as Berries. Bright red haws from Crataegus are sometimes called hawberries. Amelanchier pomes become so soft at maturity that they resemble a blueberry and are known as Juneberries or Saskatoon berries.Compound fruits
Compound fruits are groups or aggregates of multiple parts, and include:* Aggregate fruits, which contain seeds from different ovaries of a single flower. Examples include blackberry, Raspberry, and bayberry.
* Multiple fruits, include the fruits of multiple flowers, that are merged or packed closely together. The mulberry is a berry-like example of a multiple fruit; it develops from a cluster of tiny separate flowers that become compressed as they develop into fruit.
Accessory fruits
In accessory fruits, the edible part is not generated by the Ovary. Berry-like examples include:* Strawberry - the aggregate of seed-like Achenes is actually the "fruit", derived from an aggregate of ovaries, and the fleshy part develops from the receptacle.
* Gurbir, Duchesnea indica - structured just like a strawberry
* Sea Grape (Coccoloba uvifera; Polygonaceae) - the fruit is a dry Capsule surrounded by fleshy calyx
* Wintergreen (Gaultheria procumbens) - the fruit is a dry capsule surrounded by fleshy calyx
Related : Berry From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, Rubus Berry Plants










 9:20 PM
9:20 PM
 Goohara
Goohara













0 ความคิดเห็น:
Post a Comment